CNSL Polyurethane Solutions
Meet the demands of modern applications
Polyurethane Chemistry
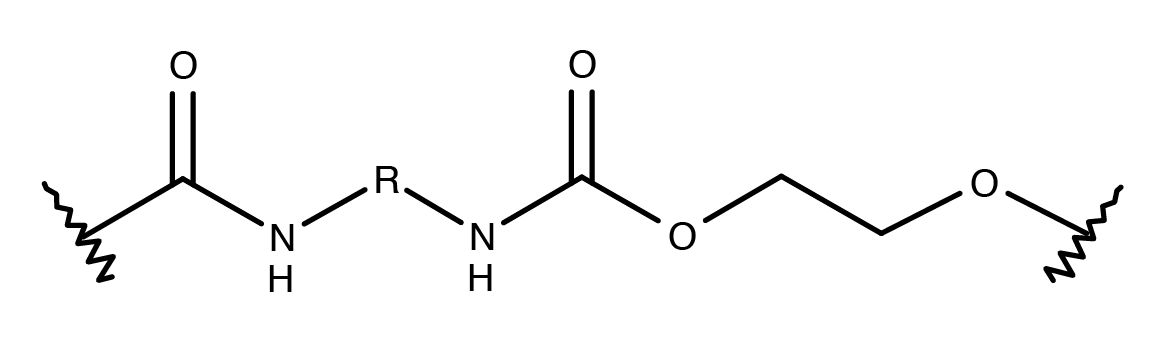
Polyurethane bonds form by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, creating a segmented polymer network:
- Soft segments (polyols/diols): Provide elasticity, resilience, and low-temperature flexibility
- Hard segments (diisocyanate/chain extender): Contribute hardness and structural strength
Common building blocks:
- Diisocyanates: TDI, MDI/PMDI, HDI, IPDI
- Polyols/diols: Polyethers, polyesters, castor-derived, polycarbonates, polycaprolactones, amine-terminated, acrylic polyols
Customizable with additives:
- Catalysts, surfactants, moisture scavengers, diluents
- Flame retardants, pigments, fillers
Key benefits:
- Mechanical strength and adhesion
- Weatherability and abrasion/tear resistance
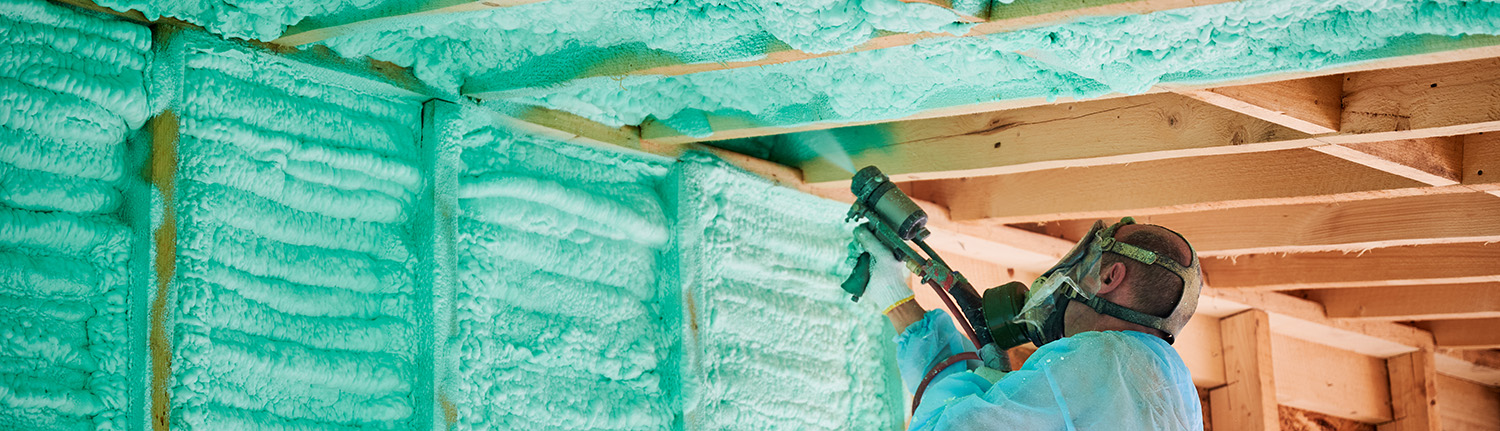
- Versatile use in coatings, adhesives, foams, elastomers, and more